|
I am a postdoctoral research scientist at Columbia University, working with Elias Bareinboim. I did my Ph.D. at Seoul National University, under the supervision of Byoung-Tak Zhang and Sanghack Lee. Prior to joining Ph.D. program, I did my master study in Computer Science at KAIST. I earned my Bachelor's degree in Department of Mathematical Sciences from KAIST. |

|
|
My research focuses on building robust, efficient, and interpretable AI systems, spanning generative models, reinforcement learning, explainable AI, and causal inference. Currently, I am working on enhancing causal reasoning capabilities and interpretability of LLMs. During my PhD, I worked on causal world model, robustness under distribution shift, and robust and efficient algorithms for causal inference. |
|
|
|
(C: conference, W: workshop, P: preprint / * equal contribution, † equal advising) |
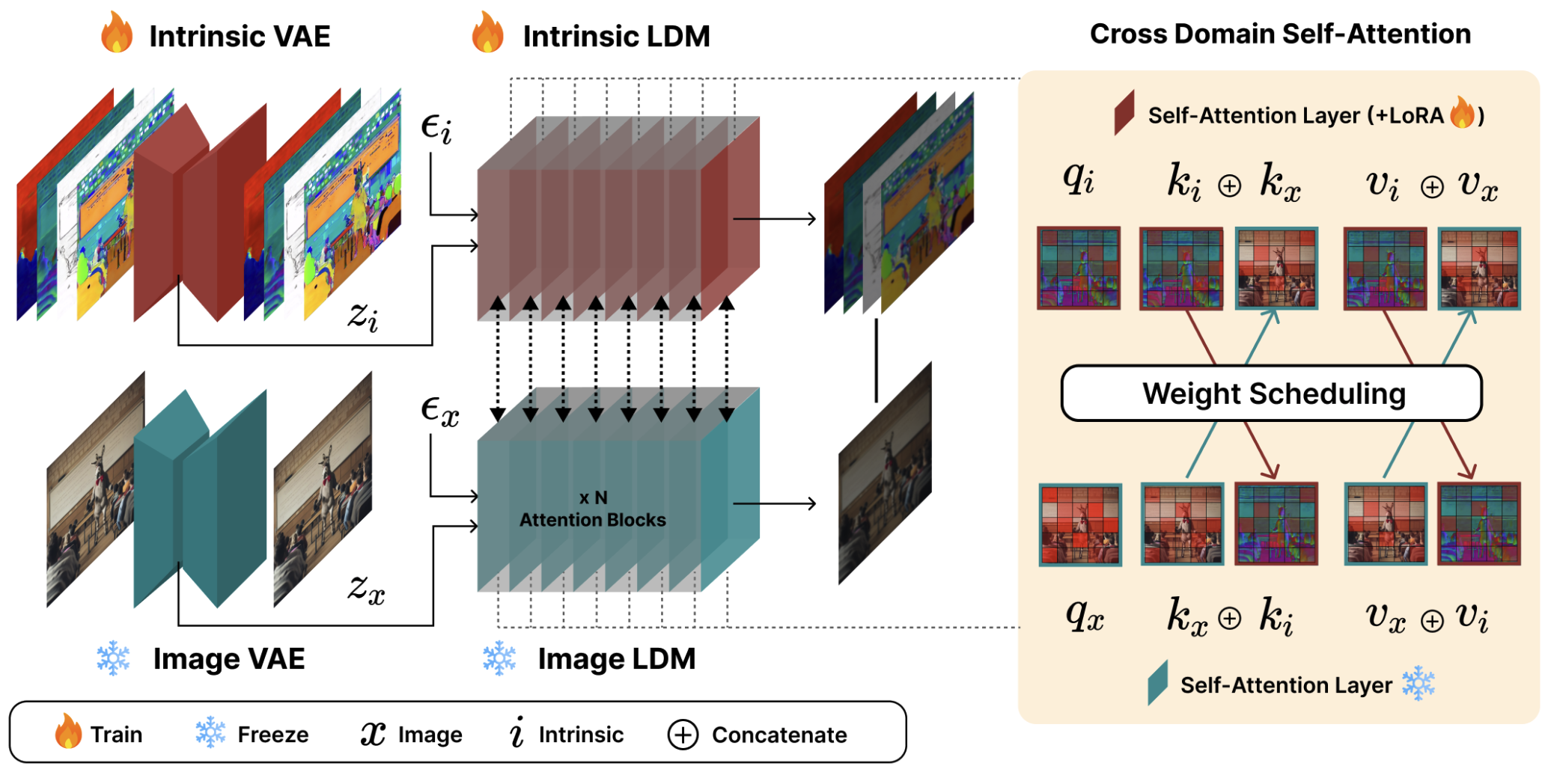
|
Hyundo Lee, Suhyung Choi, Inwoo Hwang†, Byoung-Tak Zhang†
Current image generation models trained on large datasets (e.g., Stable Diffusion) often produce spatially inconsistent and distorted images. Our idea is to leverage various intrinsic scene properties, such as depth and segmentation map, enabling the model to capture the underlying scene structure more faithfully by learning to co-generate them. As a result, our method produces a more natural layout of scenes while maintaining the fidelity and textual alignment of the base model. |
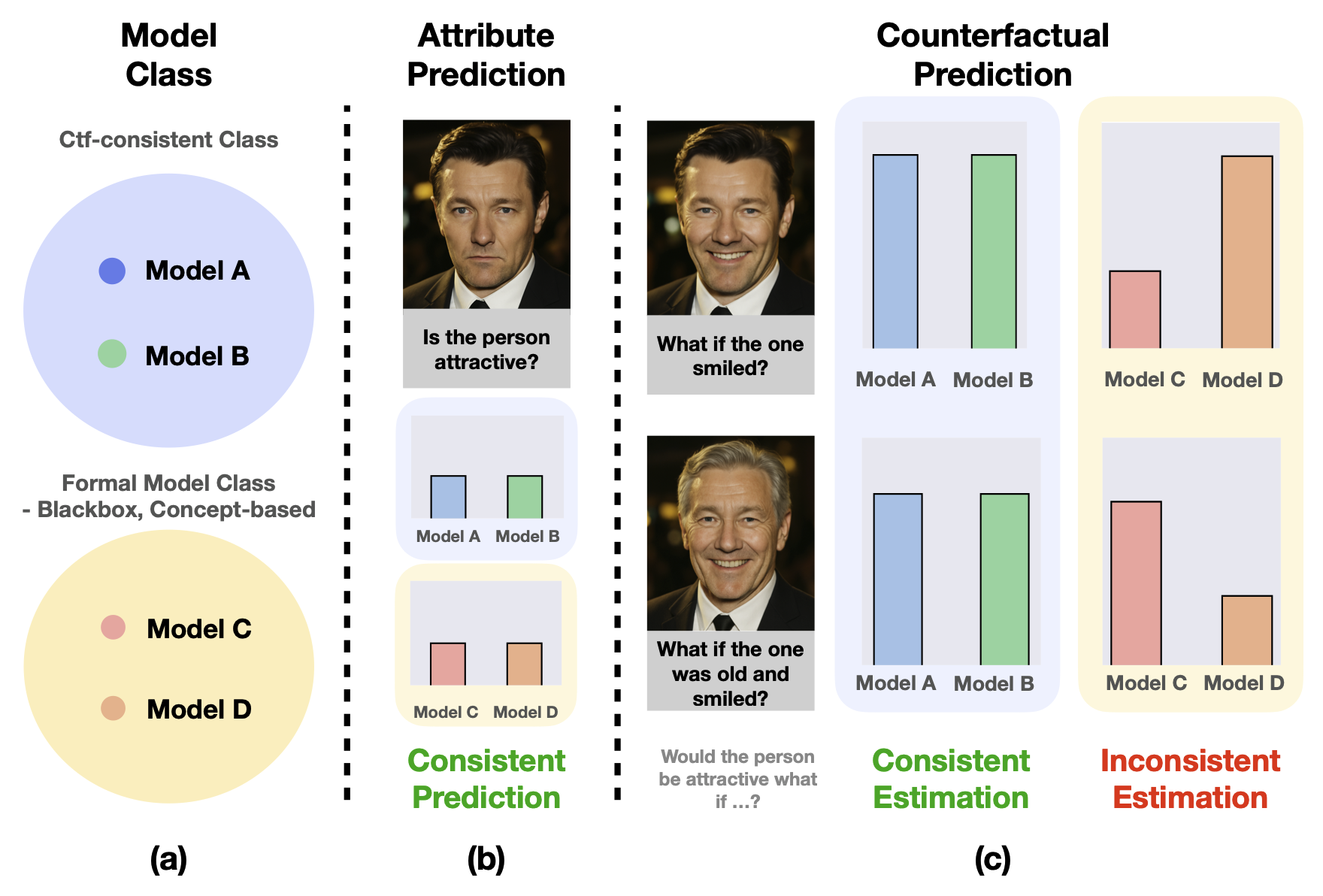
|
Inwoo Hwang, Yushu Pan, Elias Bareinboim
Can we understand the model's counterfactual predictions under hypothetical "What if" questions? Standard black-box and concept-based models cannot answer their own counterfactual questions, a fundamental limitation we prove formally. We introduce the first causal framework for building interpretable-by-design models, revealing a trade-off between interpretability and predictive accuracy. |
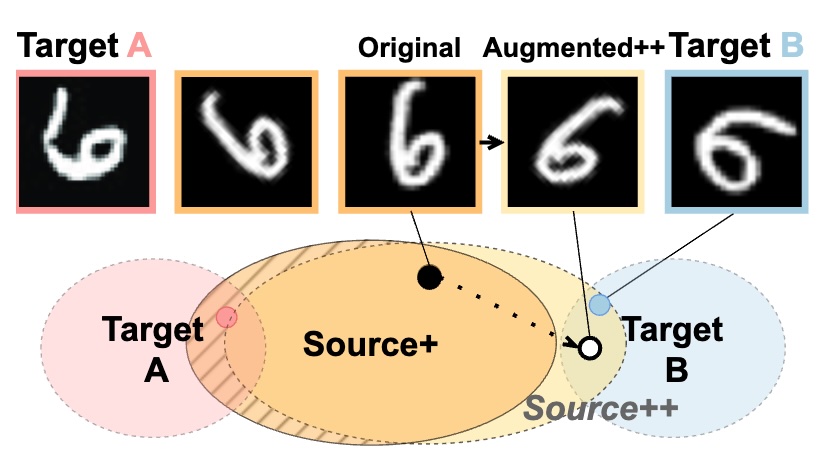
|
Dong Kyu Cho, Inwoo Hwang†, Sanghack Lee†
Data augmentation is a popular tool for improving generalization, but induces fluctuations in target domain accuracy, complicating model selection. We propose a simple model-to-model regularization with parameter-averaging framework that reduces mid-train OOD fluctuations and achieves strong generalization performance in single-source domain generalization tasks. |
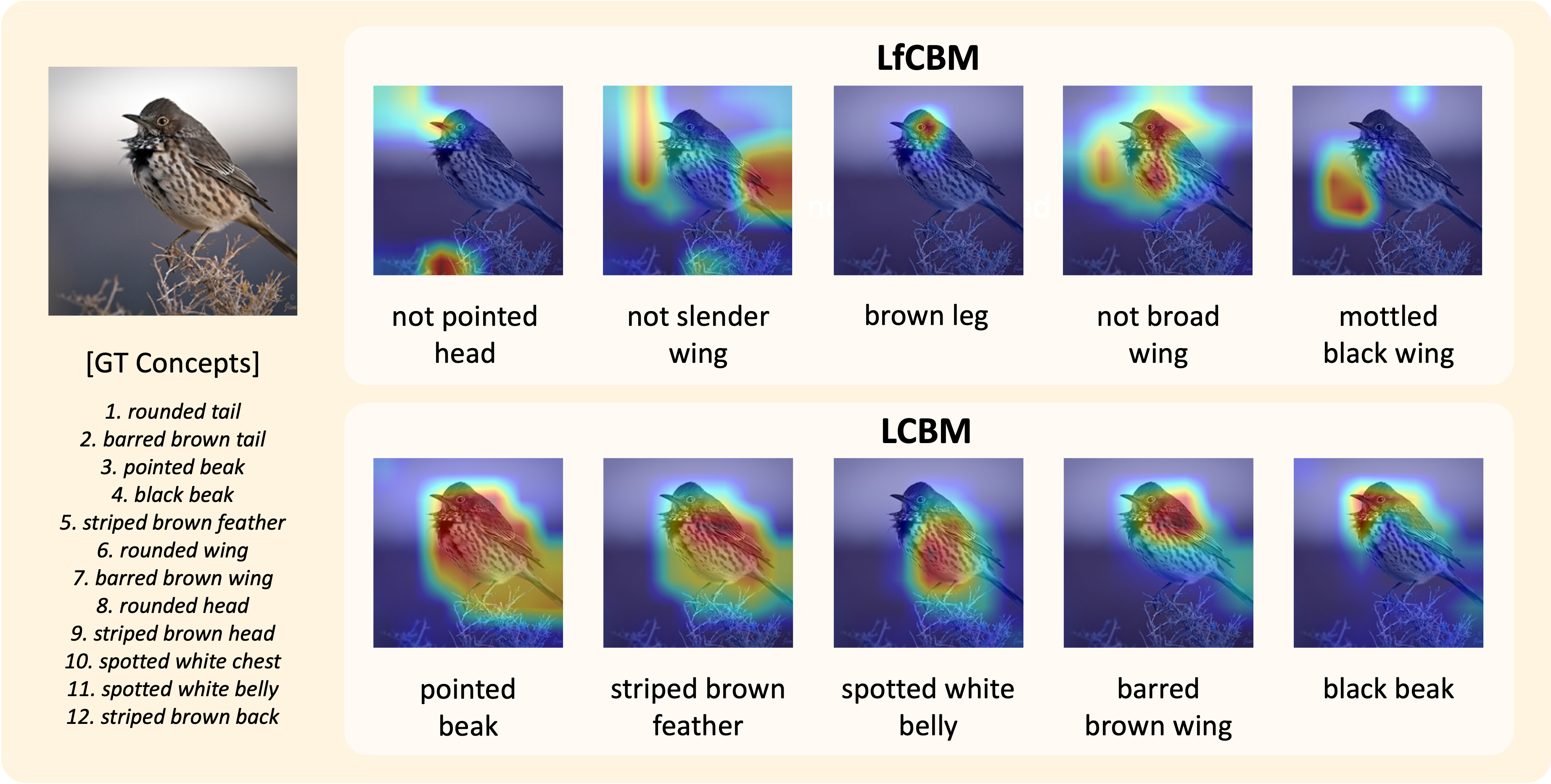
|
Sujin Jeon*, Inwoo Hwang*, Sanghack Lee†, Byoung-Tak Zhang†
|
|
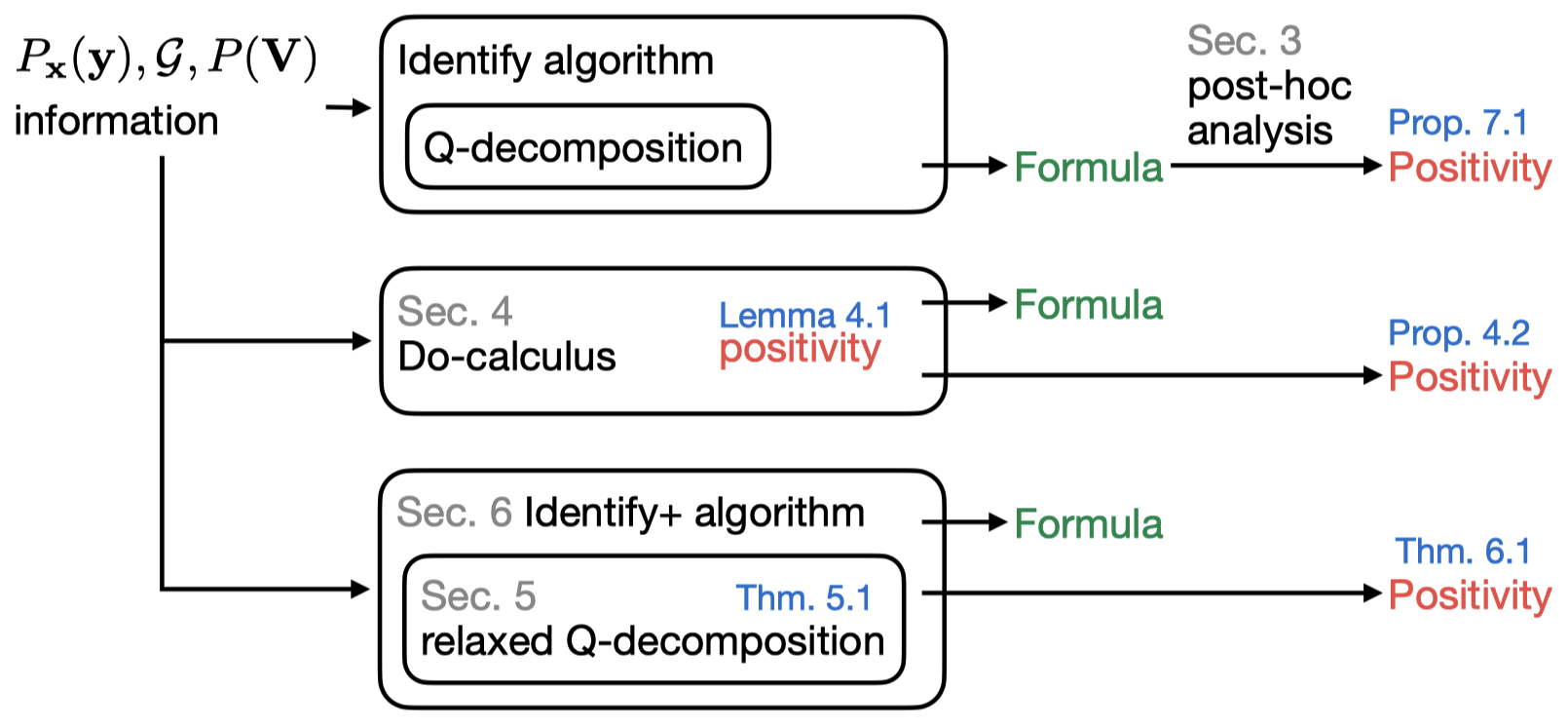
Inwoo Hwang*, Yesong Choe*, Yeahoon Kwon, Sanghack Lee
Identifying and estimating a causal effect is a fundamental problem in many areas of scientific research. A conventional assumption is the strict positivity of the given distribution, which is often violated in many real-world scenarios. We establish rigorous foundations for licensing the use of identification formulas without strict positivity, a long-standing critical assumption in causal inference. |
|
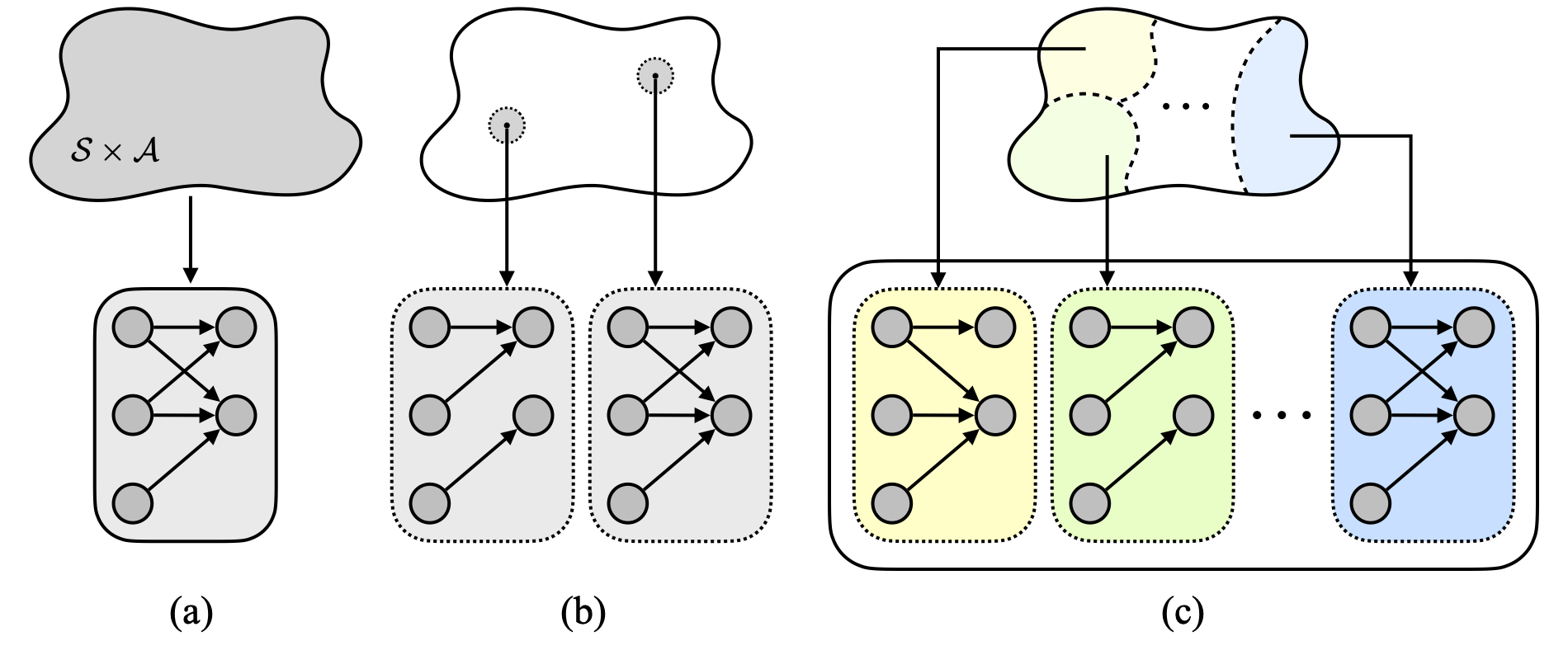
Inwoo Hwang, Yunhyeok Kwak, Suhyung Choi, Byoung-Tak Zhang†, Sanghack Lee†
Causal world model is the key to robust decision-making. However, in real-world, causal relationships are often non-stationary across different contexts. We propose a fine-grained causal dynamics learning framework where the agent is capable of understanding and reasoning about context-dependent causal relationships, thereby enabling robust decision-making. Our approach is principled and practical, with identifiability guarantees for discovering fine-grained causal relationships. |
|
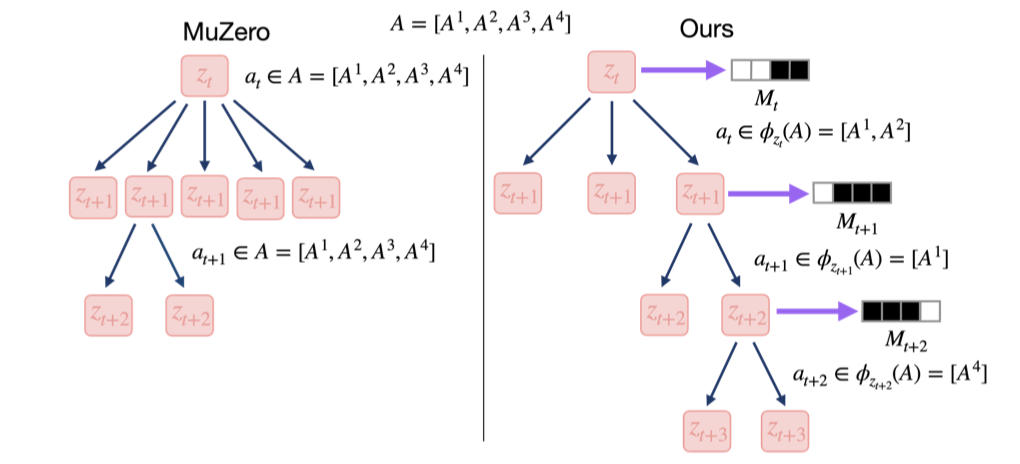
Yunhyeok Kwak*, Inwoo Hwang*, Dooyoung Kim, Sanghack Lee†, Byoung-Tak Zhang†
MCTS is a powerful tool for solving complex sequential decision-making problems. However, it suffers from the curse of dimensionality when confronted with a vast combinatorial action space. We propose state-conditioned action abstraction with latent causal world model that effectively reduces the search space of MCTS by discovering and leveraging compositional relationships between state and actions. |
|
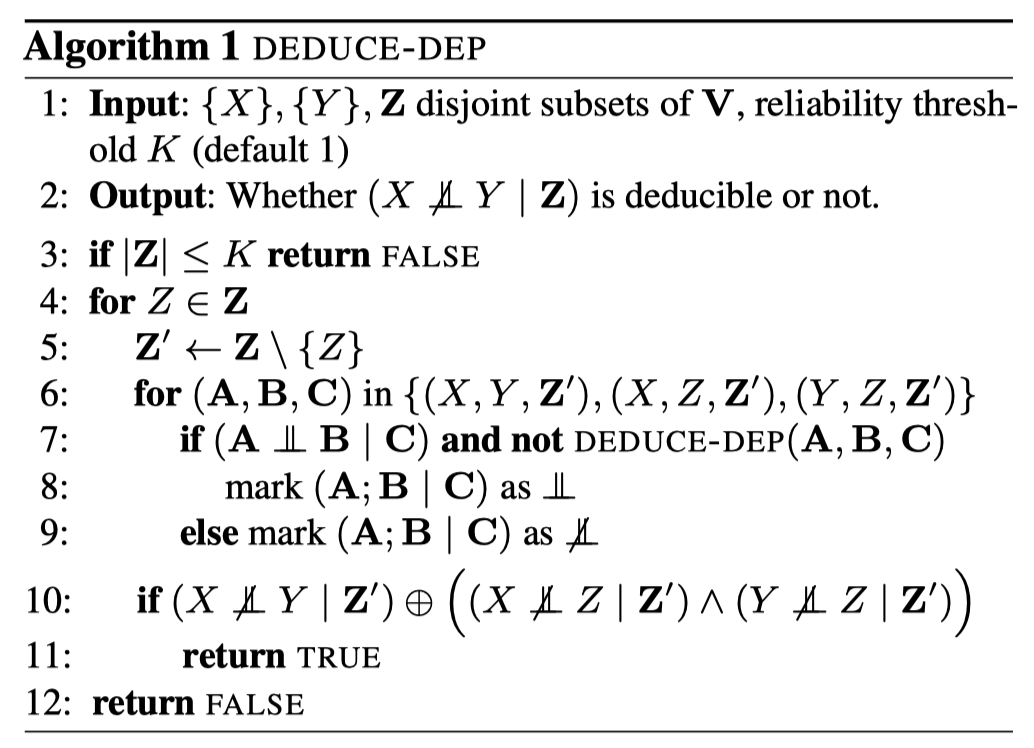
Jonghwan Kim, Inwoo Hwang, Sanghack Lee
We propose a simple yet effective plug-in module that corrects unreliable CI statements through deductive reasoning using graphoid axioms, thereby improving the robustness of constraint-based causal discovery methods. |
|
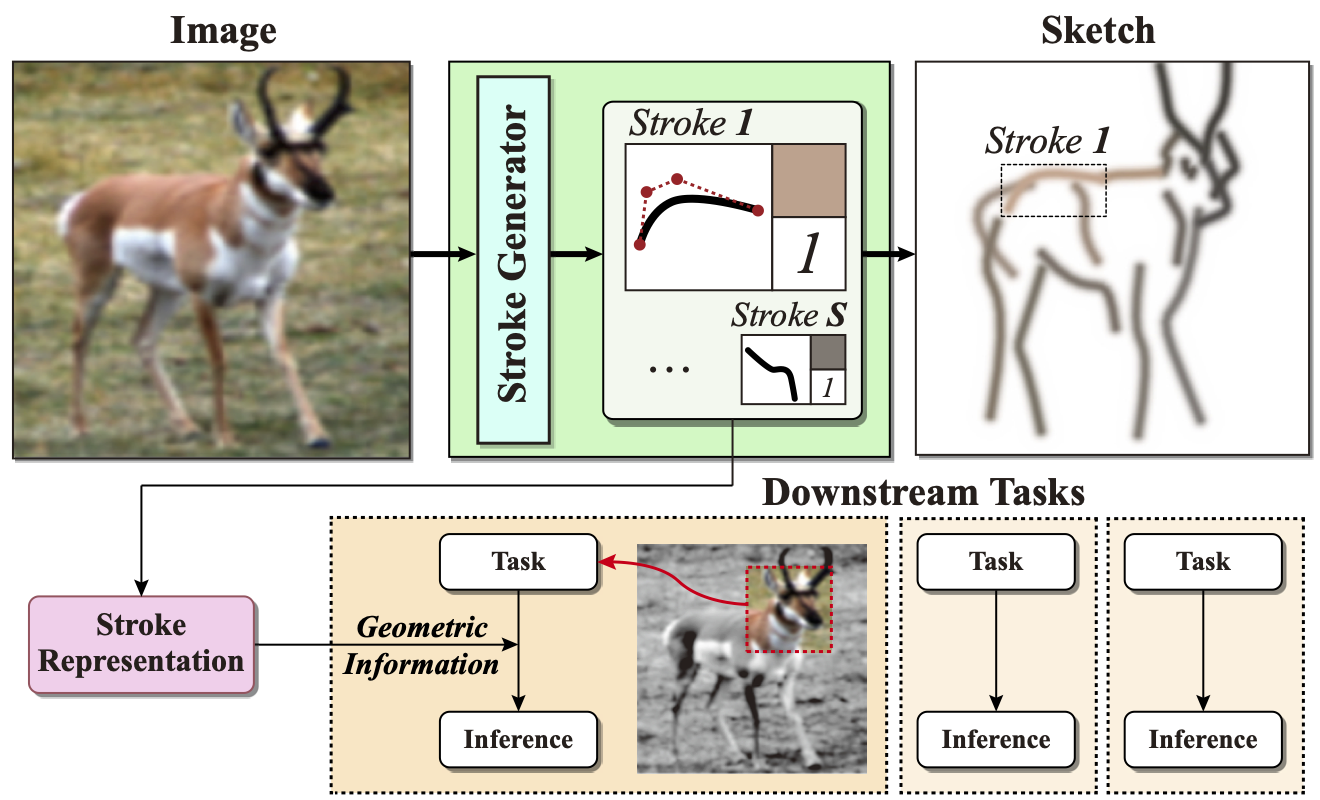
Hyundo Lee, Inwoo Hwang, Hyunsung Go, Won-Seok Choi, Kibeom Kim, Byoung-Tak Zhang
Inspired by human behavior that depicts an image by sketching, we propose a novel representation learning framework that captures geometric information of the scene, such as distance or shape. |
|
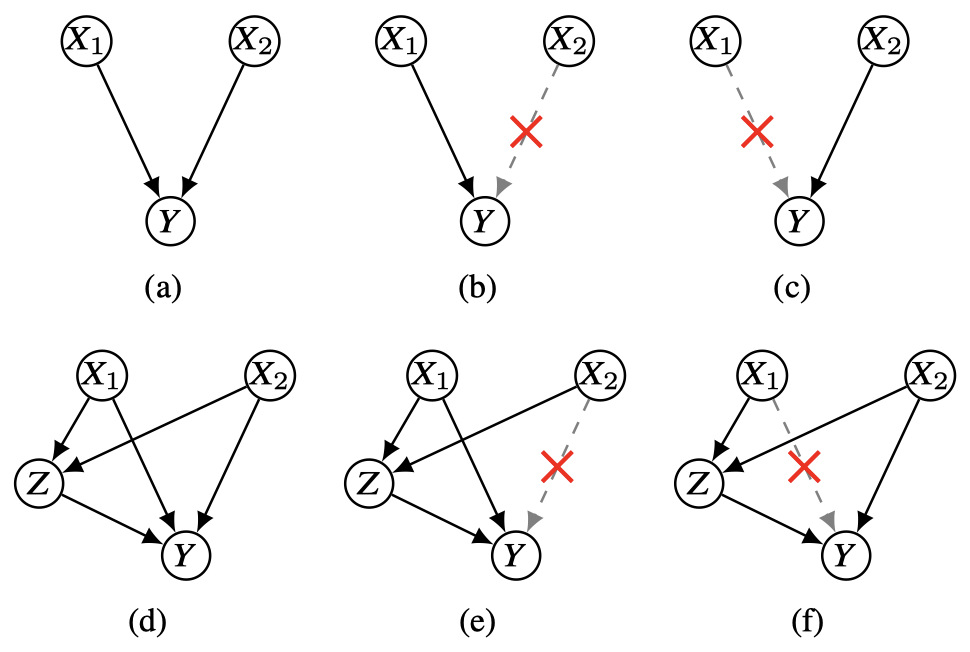
Inwoo Hwang, Yunhyeok Kwak, Yeon-Ji Song, Byoung-Tak Zhang†, Sanghack Lee†
Local independence (e.g., context-specific independence) provides a way to understand fine-grained causal relationships, but it has mostly been studied for discrete variables. We define and characterize local independence for continuous variables, provide its fundamental properties, and propose a differentiable method to discover it. |
|
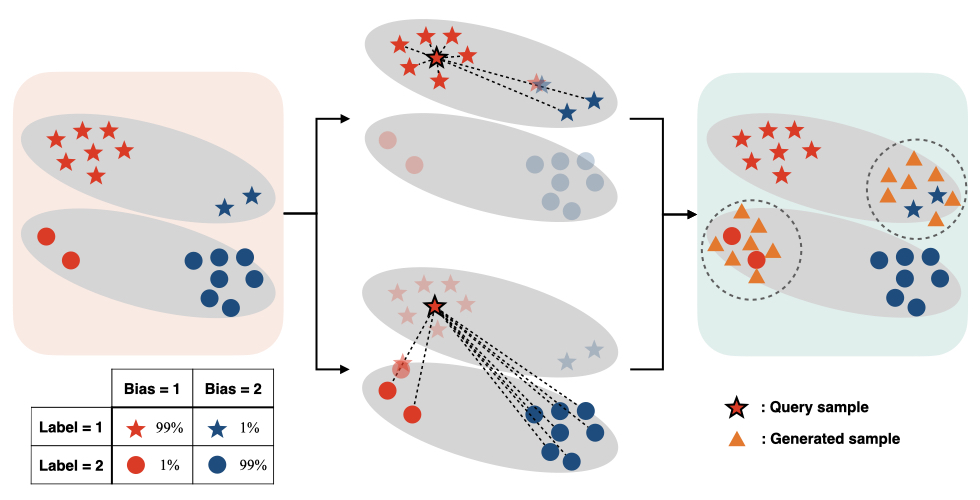
Inwoo Hwang, Sangjun Lee, Yunhyeok Kwak, Seong Joon Oh, Damien Teney, Jin-Hwa Kim†, Byoung-Tak Zhang†
Neural networks trained with ERM often learn unintended decision rules when trained on a biased dataset where the labels are strongly correlated with undesirable features. We propose a novel debiasing method that applies mixup to the selected pairs of examples, utilizing a contrastive loss designed to amplify reliance on biased features. |
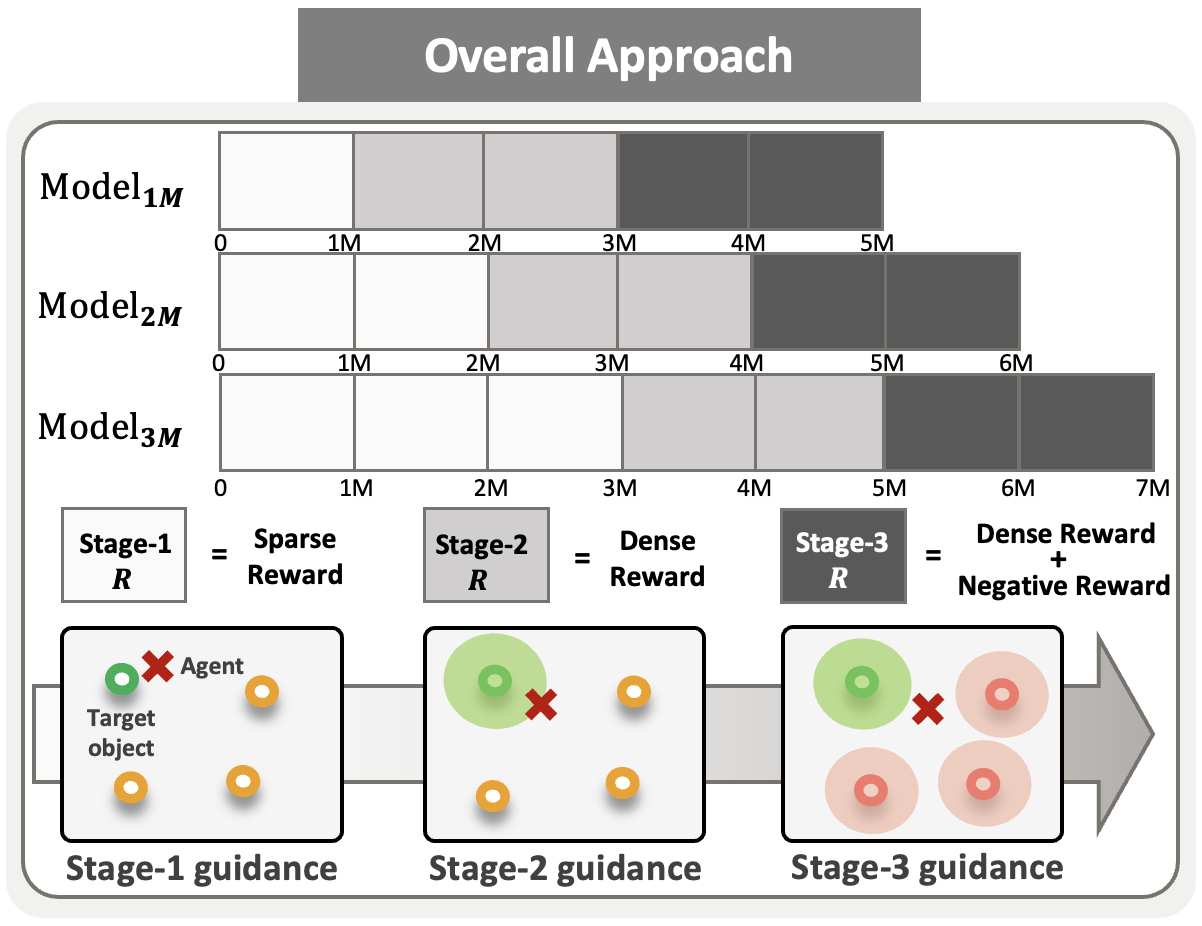
|
Junseok Park, Inwoo Hwang, Min Whoo Lee, Hyunseok Oh, Minsu Lee, Youngki Lee, Byoung-Tak Zhang
|

|
Sangjun Lee, Inwoo Hwang, Gi-Cheon Kang, Byoung-Tak Zhang
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The source of this website is from here. |